2023-08-28 09:48
Source: The Paper, Media
According to CCTV news, at 13:00 local time on August 24 (12:00 Beijing time), the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan started to discharge nuclear contaminated water into the sea.

▲Image source: CCTV News
Japan's nuclear sewage discharge will last for at least 30 years. According to the plan, the Japanese government will discharge a total of 31,200 tons of nuclear contaminated water in 4 times in 2023. The first batch is planned to discharge about 7,800 tons, which will be discharged for 17 consecutive days from August 24.
According to the news released by Tokyo Electric Power Company, today's discharge of nuclear contaminated water is expected to be 200 to 210 tons, and the daily discharge will be announced the next day. The first stage of sea discharge will last for 17 days, with a total discharge of about 7,800 cubic meters of nuclear-contaminated water.
Gao Zhiguo, president of the China Society for the Law of the Sea and former judge of the International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea, said that from the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant in Japan in 2011 to when Japan decided to discharge the sea in 2021, the nuclear polluted water has accumulated about 1.38 million tons. And it increases by about 100 tons every day, and its more than 1,100 water storage tanks will probably have no storage space by this year. Because Japan has never disclosed real data, there are about 1.5 million tons of nuclear-contaminated water now, and the discharge time may be as long as 30 to 50 years. Now the biggest concern of the international community, including neighboring countries and stakeholders, is that these nuclear and radioactive elements and substances enter the marine environment.
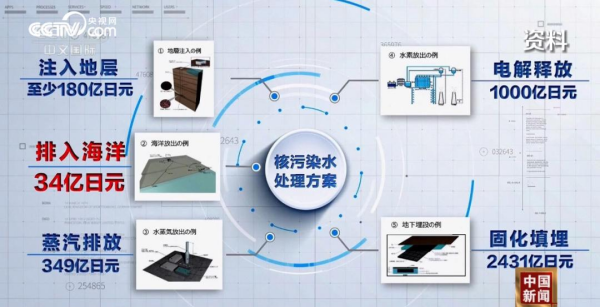
The most selfish of multiple choices, Japan's plan to discharge nuclear contaminated water into the sea is constantly advancing amidst opposition from countries all over the world and its own people. After the Fukushima nuclear accident, experts from various countries have successively proposed five solutions. In addition to discharging nuclear-contaminated water into the ocean, formation injection, steam discharge, electrolysis release, and solidification landfill are all feasible options. In the face of this difficult problem to be solved, Japan chose the cheapest one.
Zhao Shunping, a senior engineer at the Radiation Environment Monitoring Technology Center of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment, said in an interview with a reporter from CCTV's "News+" that direct discharge into the sea is the most unfavorable solution for human beings, especially for neighboring countries in the Pacific Ocean. Nor is it an optimal solution for the Japanese public. "The Japanese government's approach is an extremely selfish act that only cares about itself and ignores others."
▲Image source: CCTV
Nuclear sewage contains 64 kinds of nuclear radioactive elements :
Studies have shown that Fukushima nuclear-contaminated water contains 64 kinds of radioactive elements, and more than 70% of them exceed the standard, and there are no effective treatment technologies for many nuclides.
Masashi Goto, a Japanese engineering and technical expert, is engaged in the design of nuclear reactor containment, and has been paying attention to the dynamics of the Fukushima nuclear polluted water discharge plan. He believes that the so-called "treated water" treated by multi-nuclide removal equipment not only contains tritium that cannot be removed, but also contains a variety of other radioactive substances. The harm to the human body after entering the human body cannot be underestimated.
The radioactive tritium in nuclear-contaminated water will be absorbed by seaweed to form stable organic tritium, which will be eaten by fish and shrimp and go to the human table. Bob Richmond, a research professor at the University of Hawaii at Manoa, warned that if humans ingest these radioactive materials through seafood such as lobster or oysters, they may reach levels that damage DNA and RNA, which will cause long-term cancer problems.
According to the American "Science" magazine, the half-life of cobalt-60 in nuclear-contaminated water is about 5.27 years, and it will release gamma rays during the decay process. If people are exposed to gamma rays for a long time, it will cause diseases of the blood system. The half-life of radioactive elements in nuclear-contaminated water can be as short as ten years, and the longest can reach more than 5,000 years.
Nuclear sewage reaches my country's coastal waters in 240 days. As early as 2021, the team of Academician Zhang Jianmin and Associate Professor Hu Zhenzhong of the Institute of Ocean Engineering, Shenzhen International Graduate School of Tsinghua University established a diffusion model of radioactive substances at the ocean scale from two different perspectives, macro and micro. And realized the long-term simulation of the Fukushima nuclear sewage discharge plan.
The results show that nuclear contaminated water will reach the coast of China in 240 days, and will reach the coast of North America in 1200 days, covering almost the entire North Pacific Ocean. Subsequently, it spread rapidly to the South Pacific and Indian Ocean. The high-concentration area of pollutants will extend eastward along the 35°N line, spreading from the seas near East Asia to the seas near North America.
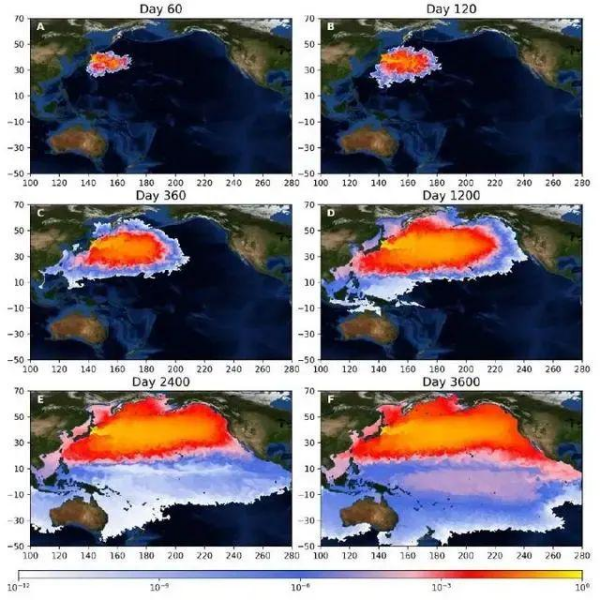
▲Macroscopic diffusion simulation results of tritium
Yu Wen, a researcher and doctoral supervisor at the School of National Security and Emergency Management of Beijing Normal University, also said that after the nuclides are discharged into the sea, they will spread away from Japan with the transport of offshore ocean currents, spreading across the Pacific Ocean and other oceans.
In addition, the German Institute of Marine Science pointed out that the coast of Fukushima has the strongest ocean currents in the world. Within 57 days from the date of discharge, the radioactive material will spread to most of the Pacific Ocean. Three years later, the United States and Canada will be affected by nuclear pollution, and 10 years later, it will spread to the global seas. Atmospheric circulation may evaporate nuclear-contaminated water into the clouds, and then turn it into rainwater and sprinkle it all over the earth. The potential harm is immeasurable.
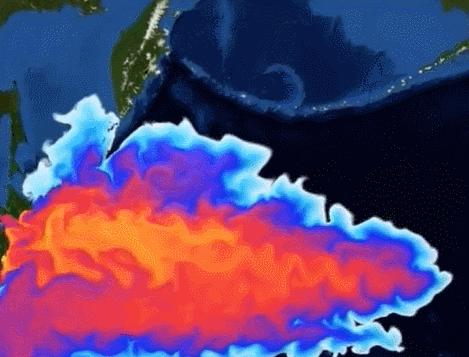
▲Image source: Xinhua News Agency
China has completely suspended the import of Japanese aquatic products :
At the regular press conference of the Ministry of Commerce held today, the spokesperson Shu Jueting responded to the "nuclear sewage discharge" in Fukushima, Japan. She said that the Japanese government unilaterally initiated the discharge of Fukushima nuclear contaminated water into the sea. It is an extremely selfish and irresponsible act that ignores international public interests. China firmly opposes and strongly condemns this.
Shu Jueting said that Japan's move will cause unpredictable damage and harm to the global marine environment, and will further aggravate the safety risks of Japanese food, agricultural and aquatic products. The Chinese government has always adhered to the supremacy of the people and will take all necessary measures to safeguard food safety and public health.
At the same time, the General Administration of Customs has also issued an announcement today to completely suspend the import of aquatic products (including edible aquatic animals) originating in Japan from August 24, 2023 (inclusive).
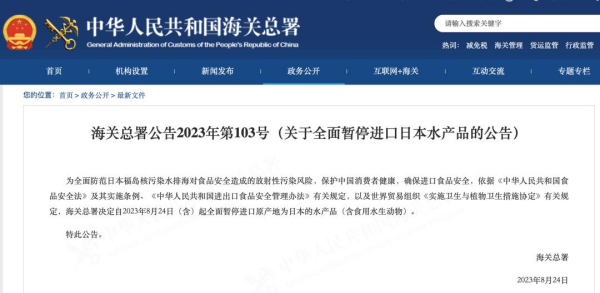
▲Image source: General Administration of Customs
Source: CCTV News, Guangming.com, the website of the General Administration of Customs, etc.
If you think this information infringes on your legitimate rights, please send evidence/ relevant qualification and requirements to info@v-cheersfilters.com, V-cheers webmaster will reply you as soon as possible.
08-31
202507-31
202506-30
202505-31
202505-15
2025